Adverbs, like adjectives, also have degrees of comparison, which are formed in the same way as the degrees of comparison of adjectives.
Remember to read How to learn English with audiobooks for FREE
Adverbs as adjectives have three degrees of comparison:
- Positive degree.
- Comparative degree.
- Superlative degree.
What do three degrees of comparison mean?
The Positive Degree is the basic, uncompared form of an adverb.
The comparative degree means that we compare objects on the basis of a common feature of these objects.
Take a look at examples:
A black horse runs faster than a white horse.
My home is bigger than your home.
This street is longer than that street.
What is the superlative degree of adverbs? The superlative degree is when we single out one item from a group of items. The subject that we highlight has the most pronounced feature.
For example:
The black horse runs the fastest of all horses.
My house is the largest of all the houses in our area.
This street is the longest in our city.
We use the comparative degree to compare the characteristics of one object with the characteristics of another object or other objects.
We use superlative to identify the object with the most pronounced (Superlative) trait.

How to form Degrees of Comparison of Adverbs
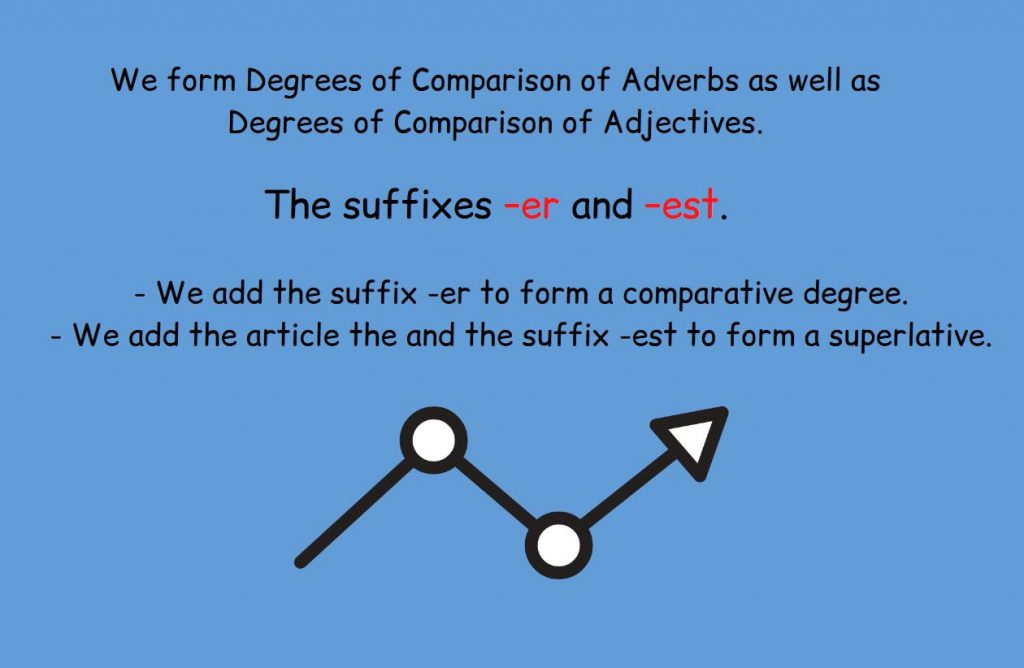
We form Degrees of Comparison of Adverbs as well as Degrees of Comparison of Adjectives.
The suffixes –er and –est.
The –er and –est suffixes are our main helpers. We use the suffixes –er and –est to form the degrees of comparisons of Adverbs that have the same form as adjectives.
- We add the suffix -er to form a comparative degree.
- We add the article the and the suffix -est to form a superlative.
Remember that we must use the to form a superlative.
Fast – faster – the fastest
Late – later – the latest
Using the words more and most.
How to form a comparative and superlative degree from adverbs that end in – ly?
We cannot add –er and –est to such adverbs …
For such adverbs, we need the auxiliary words more and most. And for the superlative, we also need the article the.
- We use more to form the comparative degree
- We use the + most to form the superlative degree
Seriously – more seriously – the most seriously
Happily – more happily – the most happily
I can make it work much more happily.
Early and Loudly
There are exceptions to this rule: such adverbs as early and loudly.
Early and loudly also end in -ly, but we can’t use more and most with them.
We form comparative and superlatives with early and loudly by adding –er and –est to them.
Early – earlier – the earliest
Loudly – louder – the loudestI left home earlier than usual.
Often, slowly, quickly.
Often, slowly, quickly are unusual adverbs too.
We can form comparative and superlative adverbs often, slowly, quickly in two ways.
We can add –er and –est to often, slowly, quickly, or use more and most.
Both options are correct.
Note, however, that the use of –er and –est is less common.
Could you go slower?
I was going more slow than she was.
Exceptions
There is a group of adverbs that form comparative and superlative degrees according to their own rules. We cannot use the methods listed above for such adverbs.
You have to learn such special adverbs.
well – better – the best
badly – worse – the worst
little – less – least
much – more – most
well – better – best
far – farther – farthest (in the meaning of distance)
badly – worse – worst
I think it just gets better and better.

Strengthening the degree of comparison of adverbs
We can strengthen the degrees of comparison of adverbs by using additional words or phrases.
Words for strengthening adverbs in a positive degree:
- Quite
- Very
- Fairly
- A little
- A bit
- Totally
- Absolutely
- Extremely
- Pretty
Words for strengthening adverbs in the Comparative degree:
- Much
- A lot
- Far
- A little
- A bit
Words for Strengthening Adverbs in the Superlative Degree:
- By far

less and the least
We can diminish the meaning of adverbs. For this, we use:
- less
- the least
We use these words in the same way we use:
- more
- the most
useful – less useful – the least useful
stupid – less stupid – the least stupid
Comparative constructions
We can do comparisons of adverbs not only in the above ways but also using special constructions:
(not) as + adverb + as
(not) so + adverb + as
Jack is as good as his master.
The food was not as bad as ever!
Please note that when we form a comparison using these constructions, we DO NOT CHANGE the adverb itself. Adverbs remain in its original form.
He looks as good as you do.
Comparative adverb + and + comparative adverb.
comparative adverb + and + comparative adverb is another formula we use to compare adverbs.
My job’s getting more and more stressful.
It looks less and less beautiful.
The cloud of dust grows bigger and bigger.
Double comparatives.
We can use another scheme called “Double Comparisons”.
We use the Dual comparatives + the to show parallel results in causation.
the + comparative adverb, the + comparative adverb / adjective
The less people speak of their greatness, the more we think of it.
The bigger we can make the wall, the better we can protect ourselves.
Superlative Degree.
We can replace the Adverb with the superlative and use the words instead:
- than ever
- anyone
- anything
Such a scheme looks like this:
comparative adverb + than ever, anyone, anything, etc.
I play video games better than anybody.
Tonight was better than anything I could’ve imagined.

Hello! If you would like to thank me for the articles I wrote, you can click Buy me a coffee. Thank you! ❤❤❤










Siempre es más fácil decirlo que hacerlo …
This website certainly has all of the information and facts I wanted concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
It’s very informative, thanks a lot ,the student from Taiwan